

Install Docker engine: yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
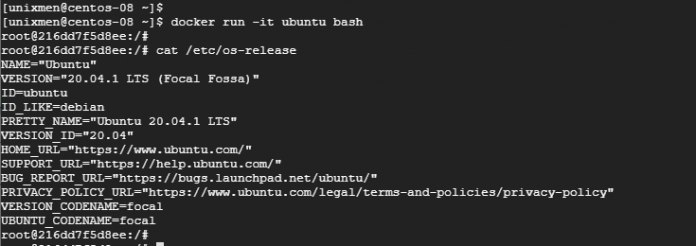
Install the yum-utils package (which provides the yum-config-manager utility) and set up the stable repository. If you’re doing this on a fresh OS, you can skip. By default is enabled, but check before starting. And it’s lighter than using Hypervisor-VM’s architecture: Installation steps However, in order to deceive the OS into believing it is operating on a real (rather than virtual) machine, another component must sit between the OS and the HW and intercept OS calls that must be mediated (such as calls that might cause a crash in another VM, or damage or corrupt shared resources, etc.).Ī hypervisor is the other component, It will do things like map physical RAM to virtual RAM, manage registers, and so on.ĭocker, on the other hand, utilizes operating system characteristics, which allow the underlying operating system to divide access to resources and processes as a distinct environment, which is (roughly) what a container is. As a result, it requires its own operating system by definition. To comprehend what Docker is and what it accomplishes, you must first comprehend the distinction between a Virtual Machine and a Container.Īs the name implies, a virtual machine (VM) is a virtual image or partition that, as closely as feasible, emulates a complete, distinct system – that is, it has its own (virtual) CPU, memory, and frequently (virtual) peripherals. Docker is an open-source project that automates the deployment of software into portable, self-contained containers that may operate on-premises or in the cloud.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
